NFT Metadata on the Flow blockchain

Doodles, a prominent player in the NFT industry, recently made headlines with their announcement of migration from the Ethereum to the Flow blockchain. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of how NFT metadata is handled on the Flow blockchain, and how it differs from other blockchains.
What is the Flow Blockchain
The Flow blockchain is a fast, efficient, and friction-less blockchain network that is designed to enable transactions that are fast and cheap. Unlike Ethereum and other EVM chains, Flow provides a seamless and smooth experience for users. It's used by many big names in the industry, such as Doodles, NFL, NBA, Ticketmaster, and Mattel. Additionally, it boasts very low transaction costs, making it an attractive option for those looking for a cost-effective blockchain solution.
How NFT metadata works on Ethereum
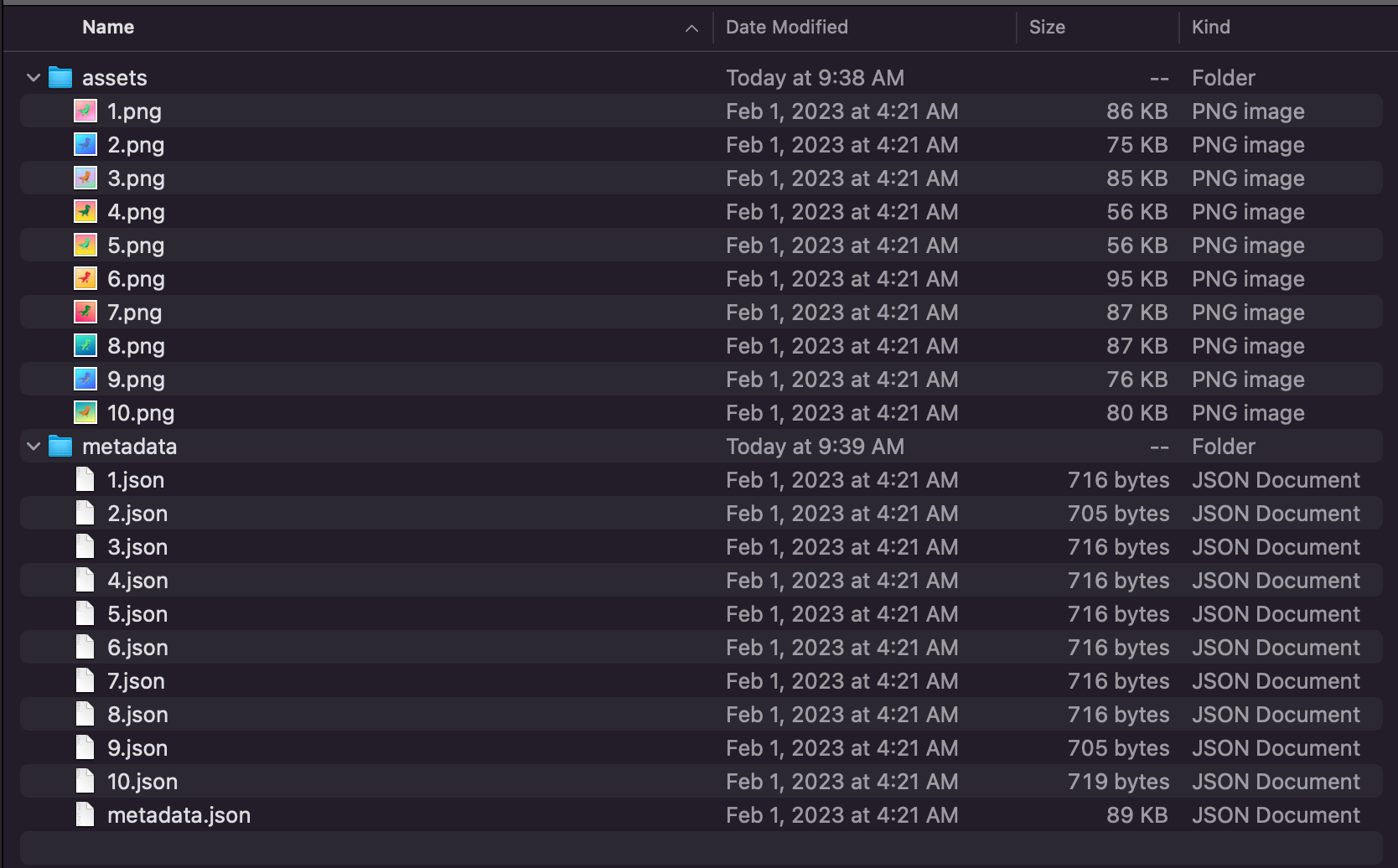
When generating a collection on Ethereum or other EVM chains, the art and metadata files are typically stored on a decentralized storage network like IPFS (or sometimes on a centralized storage like AWS S3). This is because storing large amounts of data directly on the blockchain can be very costly. A metadata file is a JSON file which contains information such as the NFT name, description, properties, and a URL to the corresponding image.
In order to reduce the amount of data stored inside a smart contract (because of cost), the smart-contract developer will store the "location" (url) of where to find all the NFT metadata. Once an NFT is minted, marketplaces will call the NFT smart-contract to so it knows where to retrieve all the NFT details from.
How metadata works on Flow
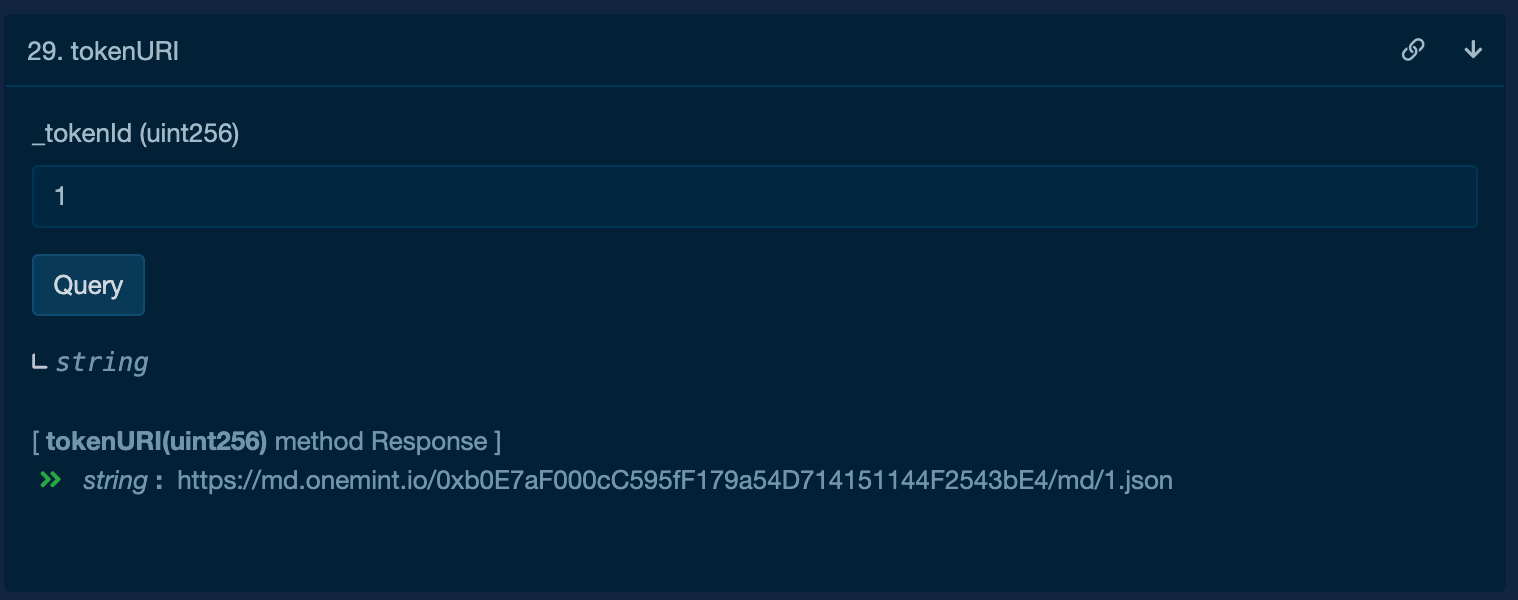
Just like Ethereum, the actual art is stored off-chain in a centralized or decentralized storage. However, the Flow blockchain differs in that all NFT metadata is stored directly on-chain. This means that there are no separate JSON files containing information such as the NFT name, description, etc. Instead, the NFT metadata is stored directly on the NFT contract on the Flow blockchain.
To enable this functionality, your NFT Flow smart contract must implement the MetadataViews interface. This allows Flow marketplaces to easily retrieve and display all of the necessary information and images for each NFT. This on-chain storage of metadata provides a more secure and transparent way to manage NFT information, and it also enables faster and more efficient marketplaces for buying and selling NFTs.
Note that the art (images/videos) are still required to be stored offline.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Flow blockchain stores NFT metadata on-chain unlike Ethereum or Polygon. However, the art, is stored off-chain, just like other blockchains.
OneMint NFT Art Generator is still a great solution to generate the art for your NFT collection. You would then ask your developer to convert the metadata we provide and add it to your NFT smart-contract.

